Hi folks, Today we will learn another interesting feature of Swift iOS and will see how we can use Use TableView in the MVVM Structure.

Introduction
In modern app development industries, the Model View View Model (MVVM) architecture pattern has become the best approach for application development.
The major reason for this significant traction is due to Its ability to separate logic and enhanced code maintainability.
While working with the MVVM architecture, using a UITableView to populate data and create the View is also one of the best options and practices in app development.
How To Implement MVVM Architecture with UITableView
Before diving into the implementation, it is a prerequisite to have a basic idea about UITableView and its implementation.
Assuming that you have a basic idea about UITableView implementation, follow the below steps to implement the MVVM pattern in the UITableView.
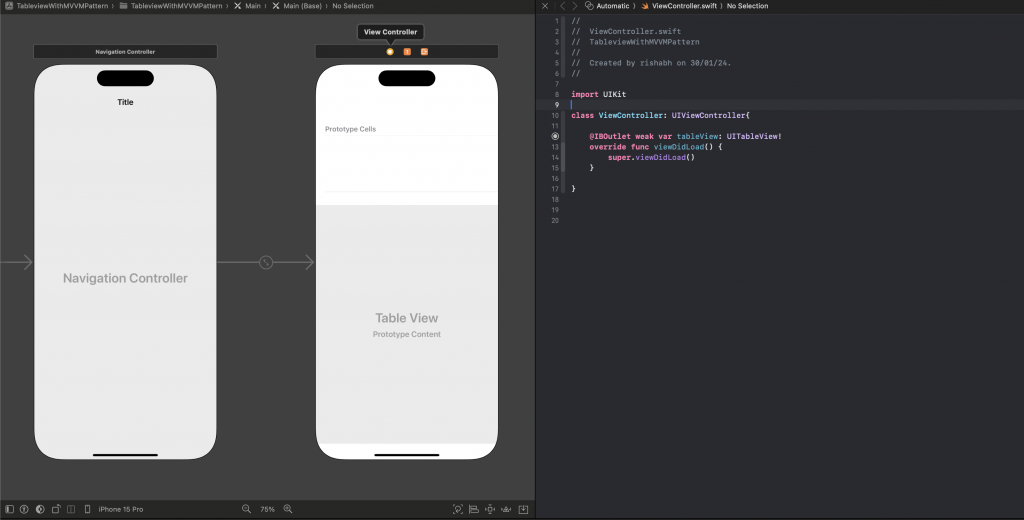
Step 1:- Create ViewController Class
Firstly, create a new ViewController class extending UIViewController. Now add the UITableView to the respective storyboard and make the connection with the ViewController.
Step 2:- Create a Model for Data
Create a Model class to store the data in a structured format.
|
1 2 3 4 |
import Foundation struct Model { let name: String } |
Step 3:- Create a ViewModel Class
Once the initial setup is complete, create a ViewModel class for your ViewController class. The ViewModel class will be used for fetching the data for our UITableView.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
class ViewControllerViewModel:NSObject{ var tableData = [Model]() func loadData(completion: (Bool) -> Void){ // Perform Api and Load the data for UITableView cells tableData.append(Model(name: "Webkul 1")) tableData.append(Model(name: "Webkul 2")) tableData.append(Model(name: "Webkul 3")) tableData.append(Model(name: "Webkul 4")) tableData.append(Model(name: "Webkul 5")) tableData.append(Model(name: "Webkul 6")) tableData.append(Model(name: "Webkul 7")) completion(true) } } |
Once the data is added for our UITableViewCells, we will use the Clousers completion handler to update our ViewController about the completion.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
class ViewController: UIViewController{ var viewModel: ViewControllerViewModel = ViewControllerViewModel() @IBOutlet weak var tableView: UITableView! override func viewDidLoad() { super.viewDidLoad() navigationItem.title = "UITable View with MVVM pattern" viewModel.loadData{ [weak self] success in tableView.reloadData() } tableView.dataSource = self.viewModel tableView.delegate = self.viewModel } override func traitCollectionDidChange(_ previousTraitCollection: UITraitCollection?) { tableView.reloadData() } } |
Step 4:- Create the View
Once we complete all the above steps, we need to populate the data on the UITableView.
For Making the view we will use our ViewModel class and populate the stored data from the model class to our UITableView cells.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
import UIKit extension ViewControllerViewModel: UITableViewDelegate, UITableViewDataSource { func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, numberOfRowsInSection section: Int) -> Int { return tableData.count } func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, cellForRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> UITableViewCell { let cell = tableView.dequeueReusableCell(withIdentifier: "cell", for: indexPath) cell.textLabel?.text = tableData[indexPath.row].name return cell } } |
Once you complete all the steps your view will look like below:-

Conclusion
So, In this article, we have now learned how can we use TableView in the MVVM Structure.
You can learn more amazing things about Swift with Mobikul Blogs.

Be the first to comment.