In this blog, we will learn how to Implement Redux state management in Flutter.
You may also check our flutter app development company page.
Introduction:-
Redux is a state management library based on Flux architecture for managing an application’s state consistently and centrally.
Implementation:-
First we need to create a new flutter project and add the following dependencies in the pubspec.yaml file.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
dependencies: flutter: sdk: flutter flutter_redux: ^0.10.0 |
Now, run the command “flutter pub get” to add the dependencies.
Add the following package to your class.
|
1 |
import 'package:flutter_redux/flutter_redux.dart'; |
Create the State:
The state of an application refers to its dynamic data, including user information, API responses, and UI state.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
class ReduxAppState { int counter; ReduxAppState({this.counter = 0}); } |
Create the Actions:
The view layer dispatches actions to modify the application’s state. They have a type and can also include payload data.
enum Actions { incrementCounter, decrementCounter }
Create the Reducer:
The reducer defines how the state should be updated based on the action type.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
ReduxAppState appReducer(ReduxAppState state, dynamic action) { if (action == Actions.incrementCounter) { return ReduxAppState(counter: state.counter + 1); } else if (action == Actions.decrementCounter) { return ReduxAppState(counter: state.counter - 1); } return state; } |
Create the Store:
The reducer function is passed to the store, and it serves as the central location for the application to store its state.
|
1 2 3 4 |
final store = Store<ReduxAppState>( appReducer, initialState: ReduxAppState(), ); |
Create the StoreProvider:
After creating the store, you can make it accessible to the rest of the application using the StoreProvider widget.
To achieve this, you need to pass the store and a child widget as arguments to the StoreProvider widget. Once done, the store will be available to the child widget and all of its descendants.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget { @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return StoreProvider<AppState>( store: store, child: Scaffold(), ); } } |
Create the StoreBuilder:
The StoreBuilder widget takes a builder function as an argument. The builder function is called whenever the state of the store changes, and it returns the updated UI.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
class ReduxStateManagement extends StatelessWidget { const ReduxStateManagement({super.key}); @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return StoreProvider<ReduxAppState>( store: store, child: Scaffold( body: StoreBuilder<ReduxAppState>( builder: (context, store) { return .......; }, ), ), ); } } |
Completed Code:-
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 |
import 'package:flutter/material.dart'; import 'package:flutter_redux/flutter_redux.dart'; import 'package:redux/redux.dart'; class ReduxAppState { int counter; ReduxAppState({this.counter = 0}); } enum Actions { incrementCounter, decrementCounter } ReduxAppState appReducer(ReduxAppState state, dynamic action) { if (action == Actions.incrementCounter) { return ReduxAppState(counter: state.counter + 1); } else if (action == Actions.decrementCounter) { return ReduxAppState(counter: state.counter - 1); } return state; } final store = Store<ReduxAppState>( appReducer, initialState: ReduxAppState(), ); class ReduxStateManagement extends StatelessWidget { const ReduxStateManagement({super.key}); @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return StoreProvider<ReduxAppState>( store: store, child: Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( backgroundColor: Colors.deepPurple, title: const Text( 'Redux State Management', style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white), ), ), body: Center( child: StoreBuilder<ReduxAppState>( builder: (context, store) { return Row( crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.center, mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center, children: [ Container( margin: const EdgeInsets.all(8), decoration: BoxDecoration( border: Border.all(), borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(4), color: Colors.deepPurple, ), child: IconButton( onPressed: () { store.dispatch(Actions.decrementCounter); }, icon: const Icon( Icons.remove, size: 28, color: Colors.white, )), ), Container( padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8), decoration: BoxDecoration( border: Border.all(), borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(4)), child: Text( 'Counter: ${store.state.counter}', style: const TextStyle(fontSize: 24), ), ), Container( margin: const EdgeInsets.all(8), decoration: BoxDecoration( border: Border.all(), borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(4), color: Colors.deepPurple, ), child: IconButton( onPressed: () { store.dispatch(Actions.incrementCounter); }, icon: const Icon( Icons.add, size: 28, color: Colors.white, )), ), ], ); }, ), ), ), ); } } |
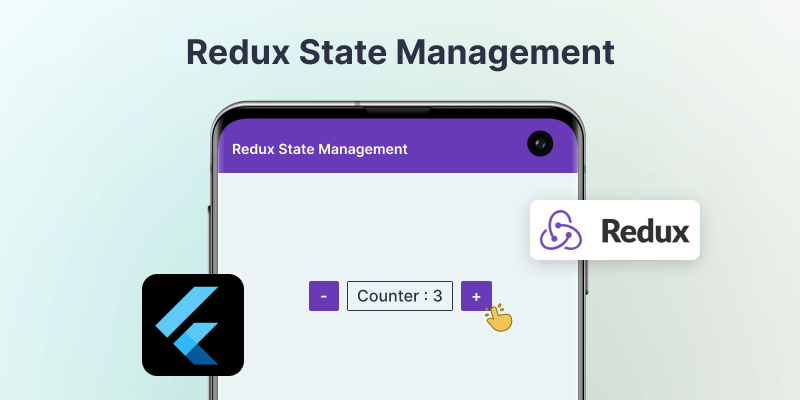
Output:-
Redux state management in Flutter
Redux is a state management library based on Flux architecture for managing an application’s state consistently and centrally.
Conclusion:-
In this blog, we discuss how to effectively manage the state of applications using the Redux library.
You can also check other blogs from here.
Thanks for reading this blog ❤️
Hope this blog helped you to better understand how to manage state using redux In Flutter.

Be the first to comment.